Navigating the complexities of government assistance programs can be daunting, especially when trying to determine eligibility for multiple benefits. One common question is whether it’s possible to receive food stamps while owning a home. This article will delve into the eligibility criteria, asset considerations, and special circumstances surrounding food stamp benefits for homeowners.
Understanding the interplay between homeownership and food stamp eligibility is crucial for individuals and families seeking financial assistance. By examining the income and asset limits, exemptions, and deductions, we can gain clarity on the factors that determine eligibility and explore strategies to maximize benefits while maintaining homeownership.
Eligibility for Food Stamps
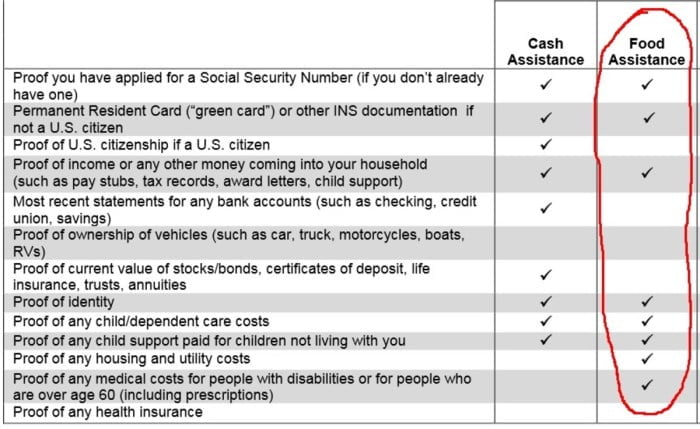
Eligibility for food stamps is determined by household income and assets. To be eligible, your household’s income must be at or below certain limits. Additionally, your household’s assets must be below specific thresholds.
Owning a house can affect your eligibility for food stamps. The value of your home is considered an asset, and it may count towards your total assets. However, there are some exceptions to this rule. For example, if you are living in your home, it may not be counted as an asset.
Types of Assets Considered
- Cash
- Bank accounts
- Stocks
- Bonds
- Mutual funds
- Real estate (excluding your primary residence)
- Vehicles
- Retirement accounts (with some exceptions)
The specific income and asset limits for food stamp eligibility vary from state to state. To find out if you are eligible, you can contact your local social services office.
Value of Assets
When determining eligibility for food stamps, the value of a house is calculated based on its fair market value. This is the estimated price the house would sell for on the open market, considering its current condition, location, and other factors.
The equity in a house is the difference between the fair market value and the amount owed on the mortgage. If the fair market value is $100,000 and the mortgage balance is $50,000, the equity is $50,000.
For food stamp purposes, the value of a house is reduced by the amount of any outstanding mortgages or other liens against the property. This is because these debts reduce the owner’s equity in the house.
Methods of Calculating Asset Value
There are three main methods for calculating the value of assets for food stamp purposes:
- Fair market value: This is the estimated price the asset would sell for on the open market.
- Equity value: This is the fair market value minus any outstanding debts against the asset.
- Net value: This is the fair market value minus any outstanding debts against the asset, plus any other allowable deductions.
The net value is the most commonly used method for calculating the value of assets for food stamp purposes.
| Method | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Fair market value | Estimated price the asset would sell for on the open market |
| Equity value | Fair market value
|
| Net value | Fair market value
|
Exemptions and Deductions
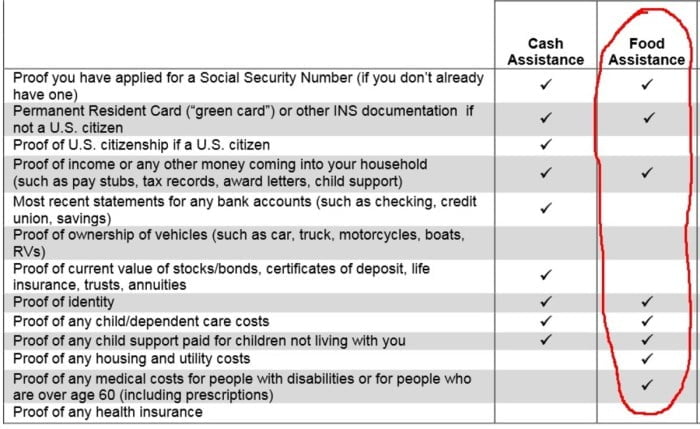
Exemptions and deductions play a crucial role in determining food stamp eligibility by reducing the value of countable assets.
These measures ensure that individuals and families with certain assets can still qualify for assistance.
Exemptions are specific categories of assets that are not counted towards the asset limit. Deductions, on the other hand, are expenses that can be subtracted from the value of countable assets.
Exemptions
- Homestead Exemption: The primary residence is exempt up to a certain value, which varies by state.
- Vehicle Exemption: One vehicle per household is exempt, regardless of its value.
- Burial Plots: Burial plots for the applicant and immediate family members are exempt.
- Retirement Accounts: Qualified retirement accounts, such as 401(k)s and IRAs, are exempt.
Deductions
- Mortgage or Rent: Outstanding mortgage or rent payments can be deducted from the value of a home.
- Medical Expenses: Unreimbursed medical expenses exceeding $3,500 per year can be deducted.
- Child Support: Child support payments made by the applicant can be deducted.
- Dependent Care: Expenses for the care of dependents can be deducted.
By applying exemptions and deductions, the value of countable assets can be significantly reduced, thereby increasing the likelihood of food stamp eligibility.
Special Circumstances
Homeowners may encounter special circumstances that affect their food stamp eligibility. These include age, disability, and other factors that can impact their ability to meet income and asset requirements.
For example, elderly or disabled individuals may have reduced income or higher medical expenses, making it difficult to meet the income limit. In such cases, they may qualify for higher deductions or exemptions that reduce their countable income and assets.
Age
Individuals aged 60 or older may qualify for higher deductions for medical expenses, housing costs, and other essential expenses. This can help them meet the income limit even if their total income exceeds the standard limit.
Disability
Disabled individuals may qualify for higher deductions for medical expenses, transportation costs, and other disability-related expenses. They may also be eligible for an additional deduction for work expenses if they are employed.
Other Factors
Other factors that may be considered include:
- Household size
- Child care expenses
- Educational expenses
- Temporary income fluctuations
In these cases, homeowners may be able to provide documentation to support their circumstances and request an adjustment to their income and asset calculations.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, owning a home does not automatically disqualify individuals from receiving food stamps. However, the value of the home, equity, and other assets must be carefully considered. Exemptions and deductions can play a significant role in determining eligibility. Special circumstances, such as age, disability, and household composition, may also be taken into account.
By understanding the eligibility criteria and available resources, individuals can navigate the process effectively and access the support they need to meet their nutritional needs while maintaining their housing stability.
FAQs
Do I need to sell my house to qualify for food stamps?
No, owning a house does not automatically disqualify you from receiving food stamps. The value of your home, equity, and other assets will be considered when determining eligibility.
How is the value of my house calculated for food stamp purposes?
The value of your house is typically calculated using the fair market value, which is the estimated price it would sell for in the current market.
Are there any exemptions or deductions that can reduce the value of my assets?
Yes, there are several exemptions and deductions that can reduce the value of your assets for food stamp purposes, including the value of your primary residence, retirement accounts, and certain vehicles.
What special circumstances may affect my food stamp eligibility as a homeowner?
Special circumstances such as age, disability, and household composition may be considered when determining food stamp eligibility for homeowners. For example, elderly or disabled individuals may have higher asset limits.